js数组遍历十种方法
本文共 3797 字,大约阅读时间需要 12 分钟。
1. some()
遍历数组,只要有一个以上的元素满足条件就返回 true,否则返回 false ,退出循环
对数组中每个元素执行一次ok函数,知道某个元素返回true,则直接返回true。如果都返回false,则返回false
检查整个数组中是否有满足元素。
private some(id: number) { const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 198, cityName: '上海'} ] let result = arr.some((item: any) => { return item.cityId === id }) console.log(`传入:${id},结果:${result}`) } 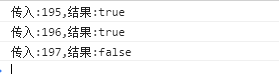
2. every()
遍历数组,每一个元素都满足条件 则返回 true,否则返回 false
private every() { const arr = [1,2,3,4,5] let result = arr.every((item: any) => { return item > 0 }) console.log(`结果:${result}`) } ![]()
private every() { const arr = [1,2,3,4,5] let result = arr.every((item: any) => { return item > 10 }) console.log(`结果:${result}`) } ![]()
3. forEach()
- 数组里的元素个数有几个,该方法里的回调就会执行几次
- 第一个参数是数组里的当前元素,第二个参数为数组里当前元素的索引值,第三个参数则是它自己
- 没有返回值,本质上等同于 for 循环,对每一项执行 function 函数。即map是返回一个新数组,原数组不变,forEach 是改变原数组。
- 不支持 continue,用 return false 或 return true 代替。
- 不支持 break,用 try catch/every/some 代替
- 数组自带的遍历方法,虽然使用频率略高,但是性能仍然比普通循环略低
private forEach() { type itemType = { cityId: number, cityName: string } const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 197, cityName: '上海'} ] arr.forEach((item: itemType, index: number, arr: any) => { console.log(`index:${index},item:${JSON.stringify(item)},arr:${JSON.stringify(arr)}`) }) } 
4. map()
- map() 方法返回一个新数组,数组中的元素为原始数组元素调用函数处理后的值。
- map() 方法按照原始数组元素顺序依次处理元素。
- 使用比较广泛,但其性能还不如 forEach
- 不会改变原始数组。
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] let newArr = arr.map((item: any) => { return item * item }) console.log(newArr) ![]()
5. filter()
- 方法创建一个新的数组,新数组中的元素是通过检查指定数组中符合条件的所有元素。
- 不会改变原始数组。
private filter(id: number): string { const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 197, cityName: '上海'} ] let name: string = '' arr.filter((item: any) => { if(item.cityId === id) { name = item.cityName } }) console.log(`传入:${id},结果:${name}`) return name } ![]()
6. find()
遍历数组,返回符合条件的第一个元素,如果没有符合条件的元素则返回 undefined
let arr = [1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,5,6] let num = arr.find((item:any) => { return item === 3 }) console.log(num) ![]()
let arr = [1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,5,6] let num = arr.find((item:any) => { return item === 10 }) console.log(num) ![]()
7. findIndex()
遍历数组,返回符合条件的第一个元素的索引,如果没有符合条件的元素则返回 -1
let arr = [1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,5,6] let num = arr.findIndex((item:any) => { return item === 2 }) console.log(num) ![]()
let arr = [1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,5,6] let num = arr.findIndex((item:any) => { return item === 10 }) console.log(num) ![]()
8. for…of…(ES6)
自动解构
for of不能对象用
const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 197, cityName: '上海'} ] for(const {cityId, cityName} of arr) { console.log(cityId, cityName) } 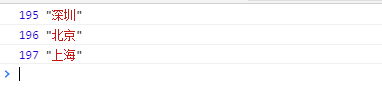
9. for…in…
for...in 语句用于遍历数组或者对象的属性(对数组或者对象的属性进行循环操作)。
for in得到对对象的key或数组,字符串的下标const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 197, cityName: '上海'} ] const obj = { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'} for(const key in arr) { console.log(`数组key-${key}`) } for(const key in obj) { console.log(`对象key-${key}`) } 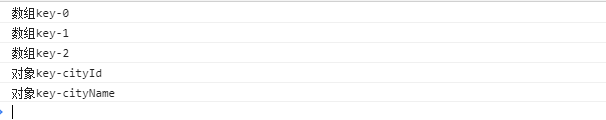
10. for
最简单的一种循环遍历方法,也是使用频率最高的一种,可优化
const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 197, cityName: '上海'} ] for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { console.log(arr[i]) } 
四种遍历方法对于100万的循环时间

for最快,但可读性比较差
forEach比较快,能够控制内容
for....of比较慢,香
for...in比较慢,不方便
转载地址:http://zdgv.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
mysql启动报错
查看>>
mysql启动报错The server quit without updating PID file几种解决办法
查看>>
mysql命令
查看>>
mysql命令==_mysql命令
查看>>
mysql命令和mysql的配置文件
查看>>
watch
查看>>